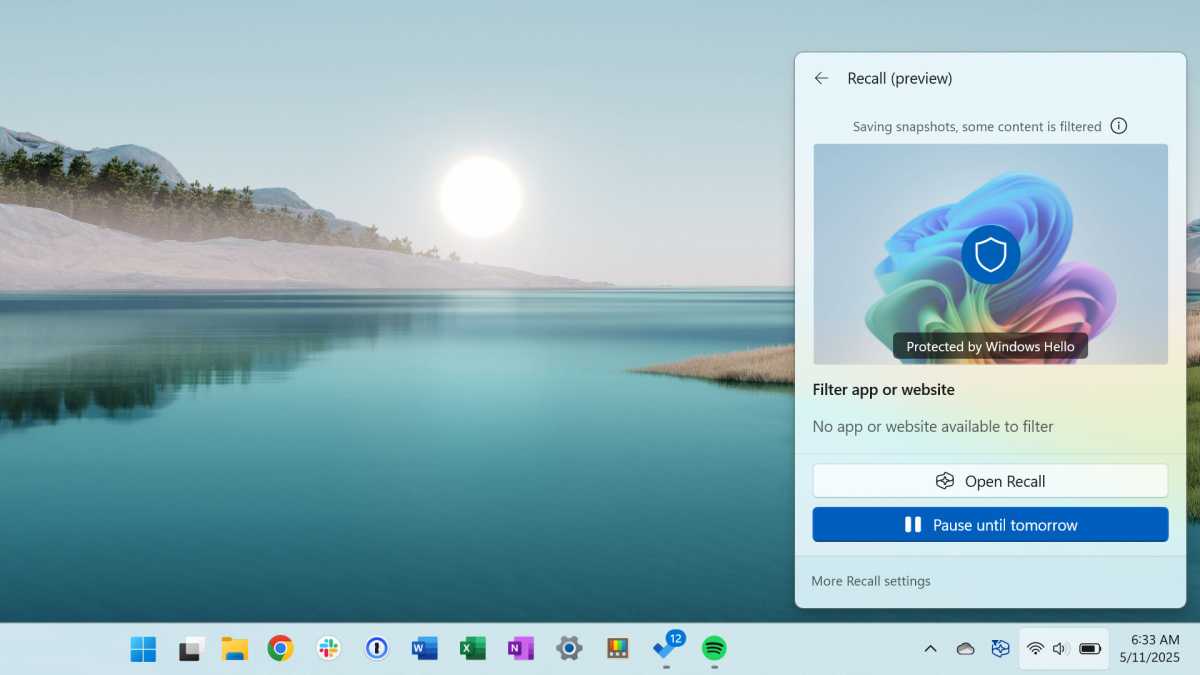
Recall is a feature in Windows 11 that regularly creates screen recordings and saves them locally. This also involves processing with AI so that users can search through the data. The aim is to make past work steps, websites, or documents retrievable via a search feature.
Microsoft first introduced Recall in 2024, but withdrew it after massive criticism due to insufficient security. The feature has been integrated again since the current versions of Windows 11 from 24H2. In Europe, it is available as an opt-in and can be completely deactivated or removed.
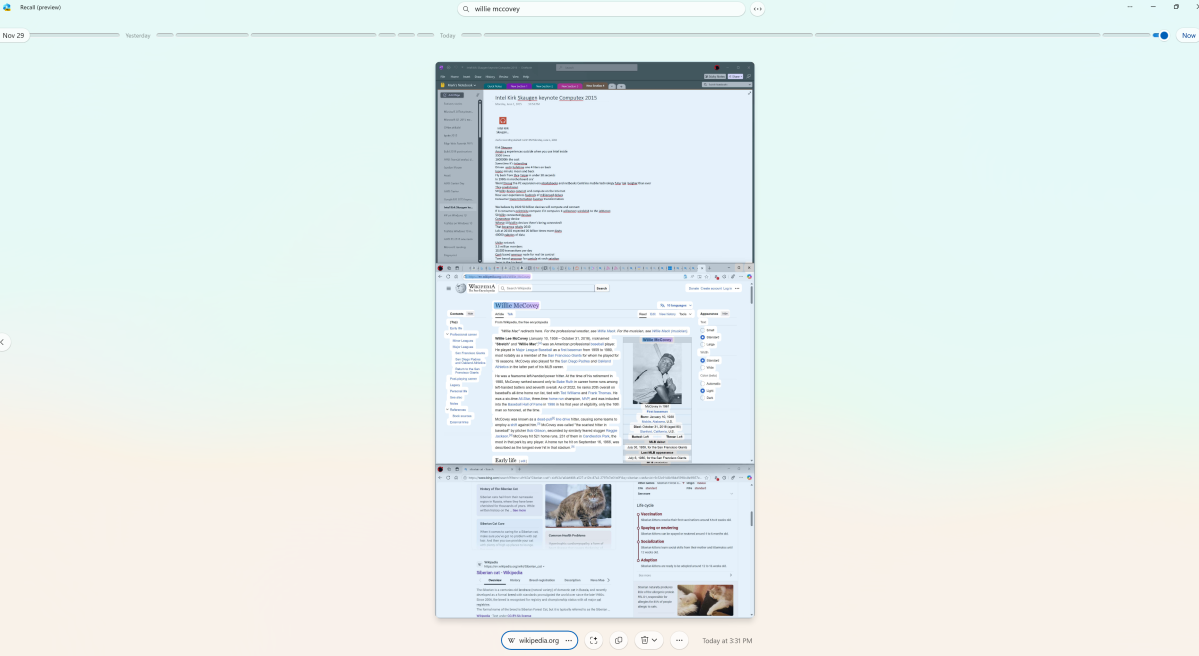
Access is via a timeline or by entering keywords in the search. The results appear regardless of the program or browser window in which the content was originally visible.
Chris Hoffman / Foundry
Tip: If you are using Windows 11 Home, you will miss out on the many advantages of the Pro version, which you can get for a significant discount at the PCWorld Software Store.
Activation and everyday use
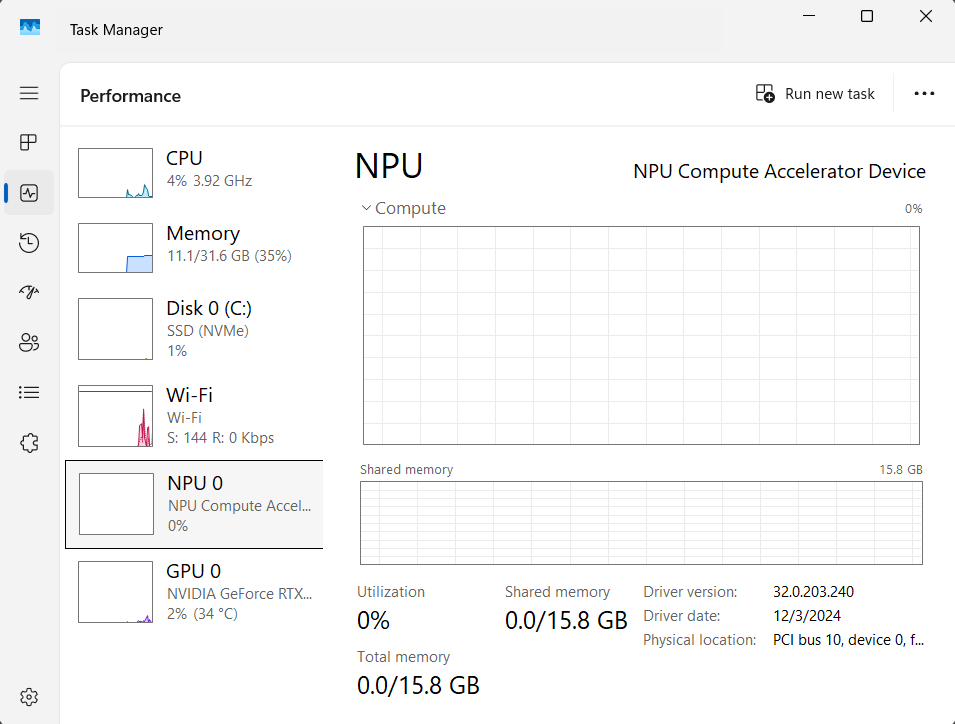
Recall is an optional feature in the current versions of Windows 11, which is only offered on Copilot models. This includes computers with a Neural Processing Unit (NPU), at least 16 gigabytes of RAM, and active drive encryption. After installing a corresponding update, the new “Recall and snapshots” section appears in the settings under “Data protection and security.” The feature can be activated here.
Sam Singleton
The system only starts to capture screenshots after this conscious consent has been given. In practice, Recall checks every five seconds to see if any content has changed and then adds new recordings. After just one working day, several hundred files are created, which can take up several gigabytes of storage space in total.
It is operated via a timeline in which you can jump back to specific points in time. Alternatively, a keyword search can be started. One example is entering “orange sofa,” whereupon Recall suggests a shopping page with the product you are looking for. Content from Office documents, PDFs, or locally saved images also appear in the hits.
Deactivation via settings and group policies
The feature can be paused or completely deactivated at any time via the settings. Companies have further options via group policies. The “Allow Recall to be enabled” policy exists there. If it is set to “Disabled,” the feature disappears completely from the system, the associated files are removed, and a restart completes the process. This method is intended for the Pro and Enterprise editions of Windows.
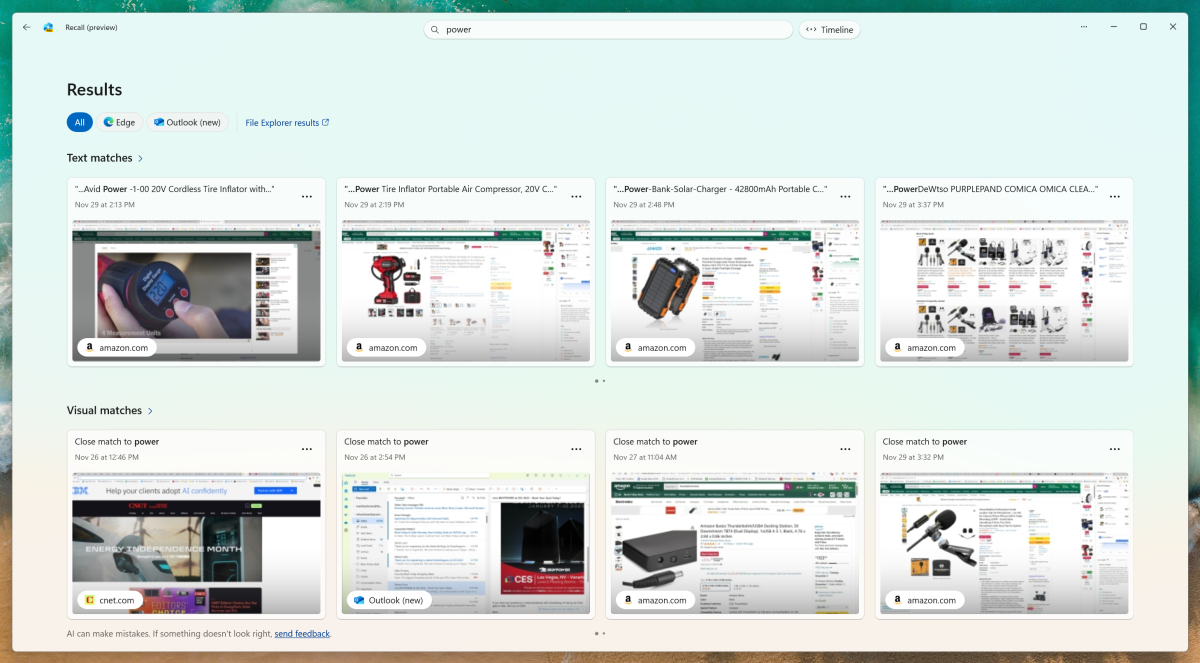
The recall search via keywords divides the results here into text and visual matches. Text matches are assigned to the applications from which the recorded content originates.
Mark Hachman / IDG
Windows 11 Home users must use the registry editor. Under “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsAI,” a new DWORD value with the name “AllowRecallEnablement” can be created and set to 0. After a restart, all components are removed. Microsoft also offers administrators the PowerShell command “Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName ‘Recall’ -Remove” which also removes the feature from the system.
Security protection
The data that Recall collects remains stored on your own computer. It is not automatically transferred to Microsoft servers or a cloud. To ensure that no one can access these recordings unnoticed, Windows requires you to log in via Windows Hello. This means that you must either enter your PIN or use a biometric method such as fingerprint or facial recognition.
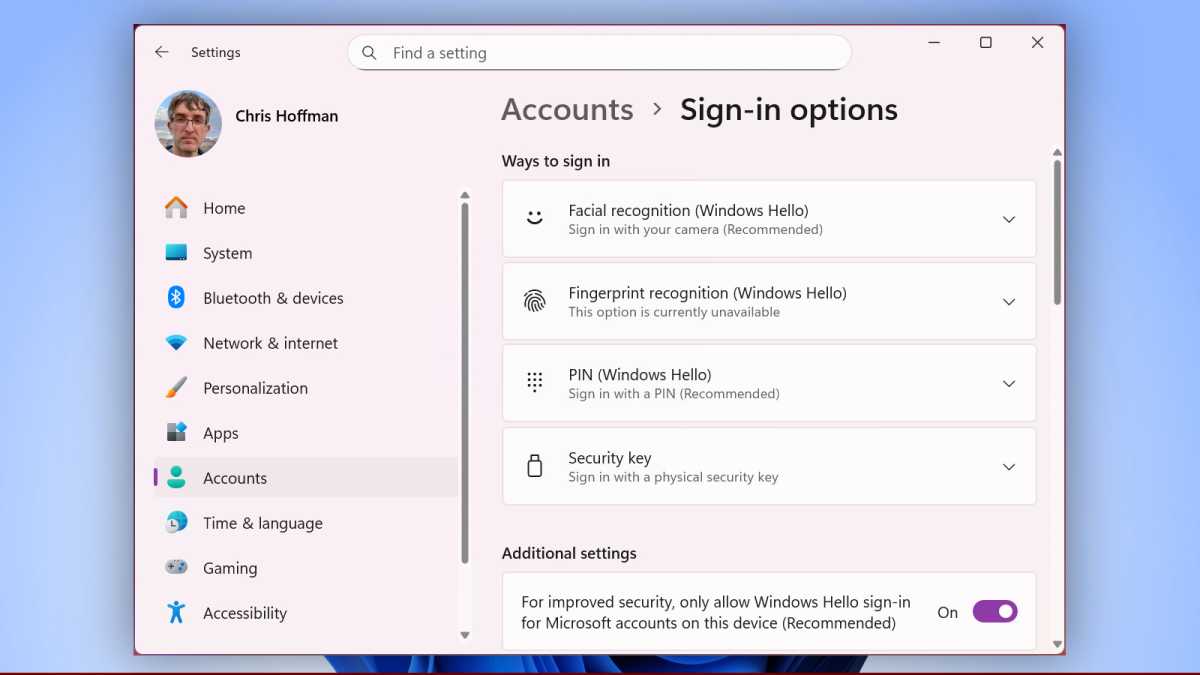
The recall search via keywords divides the results here into text and visual matches. Text matches are assigned to the applications from which the recorded content originates.
Chris Hoffman / Foundry
Windows also protects the recall data with a technology called VBS Enclave. You can imagine this as a closed area in the computer that is separated from all other programs. Only Windows itself is allowed to look into this area. This prevents external programs from simply reading the recall data. This is exactly what has happened in the past. Microsoft therefore withdrew this feature at the end of 2024.
Encryption keys are anchored in the device’s TPM chip. In theory, this prevents attackers from reading the database without a valid login. However, our tests have shown that this protection has its limits.
If a device is controlled via remote software such as Teamviewer, it is sufficient to enter the PIN to gain access to the entire recall history. Biometric procedures can be bypassed in this scenario. The risk of an external connection allowing access to all stored content remains.
Filter mechanisms and their limits
To protect sensitive data, Microsoft promises a filter that removes passwords or credit card information from the recordings. In practice, this only works to a limited extent. Although passwords are hidden in bank login windows, user names still appear.
Credit card numbers in form fields are recognized in most cases, but in emails or unprotected text documents they end up unchanged in the recordings. Account balances from online banking applications also regularly appear in the database, even if parts of the page are anonymized by the filter.
The handling of self-created password lists is also problematic. If a text file does not contain any unique keywords such as “password,” it is saved by Recall without restriction. This means that access data can be searched for in plain text if it is visible on the screen in an unprotected document.
Benefits in everyday working life
Regardless of the risks, Recall certainly offers advantages. In an environment with many applications open in parallel, the search makes it easier to find your way around. If you switch between projects, you can pick up where you left off with just a few clicks. The feature also saves time when researching on the web when dozens of tabs are open. Instead of laboriously searching through the history, a keyword is enough to open the page you are looking for.
Recall can also be helpful for users who frequently work with visual content. A designer reviewing visual material can use the keyword search to find screenshots that were only briefly displayed. In this use case, Recall replaces manual documentation of work steps.
Legal framework conditions in Europe
The delayed introduction in the European Union shows that the regulatory framework plays a central role. Data protection authorities only gave the green light after Microsoft designed the feature as an opt-in and created the option to uninstall it. Users must actively agree before Recall starts. The European version also allows the feature to be removed completely.
Mark Hachman
Additional requirements apply for companies. Recall may not be used without the consent of employees. Administrators can control the provision, but cannot force snapshots. Microsoft is thus complying with the General Data Protection Regulation, which sets particularly high standards for the processing of personal data.
Weighing up the benefits and risks
The tests so far have made it clear that Recall is a tool with considerable potential, but also with clear weaknesses. While local storage and encryption provide a solid foundation, the filters remain unreliable. Confidential information can end up in the database and be accessed remotely.
Anyone using Recall must be aware that the added convenience of seamless documentation comes with a loss of control over sensitive data.
This may be acceptable on private devices with manageable risks. In a corporate environment, however, the concerns outweigh the benefits. Recall should only be used here after careful consideration if there are clear guidelines on the use and protection of data.
Conclusion
Recall in Windows 11 is technically mature enough to be used productively, but at the same time not yet reliable enough to dispel security concerns. The feature creates transparency about past work steps, but inevitably also saves content that does not belong in a search database.
If you want to use Recall, you should check the settings carefully, adjust filters, and empty the database regularly. For security-conscious users, deactivation via group policies, registry, or Powershell remains a necessary means of minimizing risks.
It is to be expected that Microsoft will make improvements, but it is also to be expected that tools will appear that can override Recall. From our point of view, the use of Recall is currently not recommended.
Further reading: Windows Recall is too risky for your PC. I can’t recommend it






